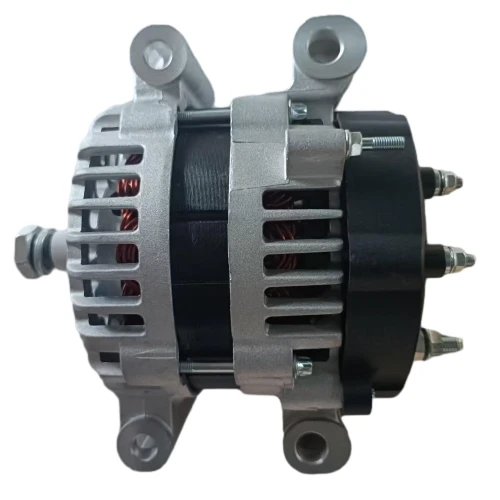
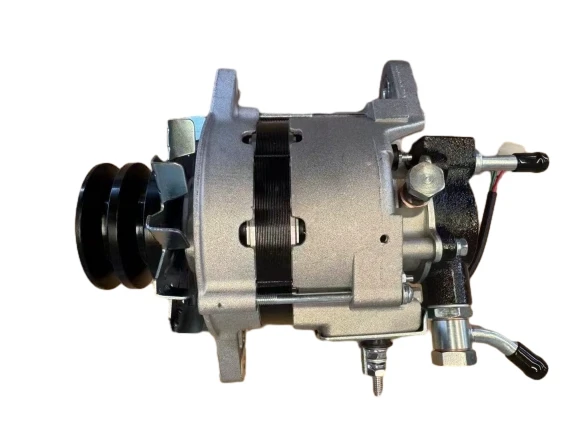
The application of automotive AC alternators runs through various aspects of vehicle operation and continues to expand with the development of automotive technology.
Ensure the operation of vehicle power system: continuous power supply, replacing batteries as the main power source. The only power source for engine operation: When the engine starts and the AC alternator reaches idle speed (about 1000 revolutions per minute), it replaces the battery as the main power source for the vehicle, directly supplying power to all electrical equipment in the vehicle. Battery charging: maintaining electrical balance.
Dynamic charging mechanism: The DC power output by the alternator charges the battery through the charging circuit, replenishing the power consumed during startup and offsetting the static power consumption of the vehicle (such as anti-theft system, clock, etc.). Voltage stability: protects precision electronic equipment.
Suppressing voltage fluctuations: Changes in engine speed (such as acceleration and deceleration) can cause fluctuations in the output voltage of the alternator. The voltage regulator quickly adjusts the excitation current (response time in milliseconds) to ensure stable output voltage and prevent voltage shock from damaging precision components such as ECU and sensors.
- Benz Alternator
- Cummins Alternator
- Wei Chai Alternator
- Heavy Truck Man Alternator
- Daf Alternator
- Howo Alternator
- Perkins Alternator
- Daewoo Alternator
- Lucas Alternator
- Mitsubishi Alternator
- Kubota Alternator
- Scania Alternator
- Yu Chai Alternator
- Volvo Alternator
- Nissan Alternator
- CONSTRUCTION MACHINERY SERIES
- Carterpillar Alternator
- XiChai Alternator
- DongFeng Alternator
- Home
- Products
- Benz Alternator
- Cummins Alternator
- Wei Chai Alternator
- Heavy Truck Man Alternator
- Daf Alternator
- Howo Alternator
- Perkins Alternator
- Daewoo Alternator
- Lucas Alternator
- Mitsubishi Altemnator
- Kubota Altemnator
- Scania Altemnator
- Yu Chai Alternator
- Volvo Alternator
- Nissan Alternator
- CONSTRUCTION MACHINERY SERIES
- Carterpillar Altemnator
- XiChai Altemnator
- DongFeng Altemnator
- About Us
- Application
- Resources
- News
- Contact
- featuredproducts