Best Car Engine Alternator – Reliable Performance for All Engines Alternator Function & Diesel Engine Solutions
- Introduction to car engine alternator
and its essential function - Core working principles of an alternator in car engines
- Key technical advantages and latest innovations in alternator design
- Market comparison of leading alternator manufacturers
- Custom alternator solutions for specific automotive applications
- Real-world application cases in passenger cars and diesel engines
- Conclusion: The future and transformative impact of car engine alternator systems
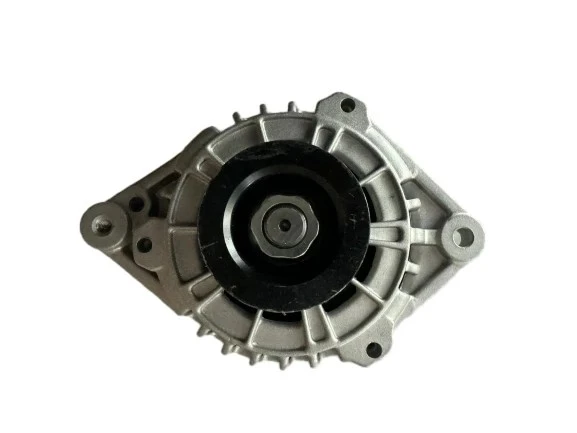

(car engine alternator)
Car Engine Alternator: The Backbone of Modern Power Supply
The car engine alternator stands as one of the most vital components in both traditional internal combustion and modern hybrid vehicles. By efficiently converting mechanical energy into electrical energy, this device ensures the ongoing operation of critical systems including lights, power windows, infotainment, and engine management electronics. Industry data reported by MarketsandMarkets indicates that the global automotive alternator market exceeded USD 9.5 billion in 2023, underlining its ubiquity and significance.
The function of an alternator in a car engine transcends mere battery charging. A healthy alternator supports vehicle reliability, fuel efficiency, and emissions reduction. On average, a standard alternator is responsible for supplying between 80 and 150 amperes—enough to simultaneously support multiple high-demand loads. Furthermore, advances in alternator technology have expanded life expectancy beyond 120,000 miles or 8 years of service, minimizing replacement frequency and ensuring long-term vehicle performance. As the automotive landscape evolves with electric and hybrid propulsion, the alternator’s adaptability to various engine architectures underscores its enduring relevance.
The Working Principles and Function Within Car and Diesel Engines
An alternator’s fundamental operation is built upon electromagnetic induction. As the engine runs, it spins a rotor inside the alternator, creating a rotating magnetic field. This movement induces an alternating current (AC), which is then rectified to direct current (DC) by a set of diodes—making it compatible with a vehicle’s battery and electronics.
In petrol and diesel engines alike, the function of the alternator begins as soon as the engine fires. Modern alternators integrate voltage regulators to maintain a steady output regardless of engine speed. In diesel engines, which often support heavier electrical loads for applications like commercial trucking or construction, alternators are engineered for increased capacity—some models deliver output upwards of 200 amperes.
When comparing the function of alternator in diesel engine with that in petrol variants, the primary distinction lies in output capacity and cooling architecture. Diesel vehicles, due to their larger electrical demands, frequently employ alternators with enhanced cooling fins, robust bearings, and customized mounting solutions. This ensures reliability even during extended idling and frequent stop-start operating conditions, which are common in heavy-duty applications.
Technical Advantages and Innovations in Alternator Technology
During the past decade, notable advancements have marked a technological evolution in alternator design. Efficiency gains of up to 30% have been achieved through the implementation of high-strength, lightweight materials and redesigned stators.
Key technical advantages include:
- Improved Efficiency: Use of rare-earth magnets and enhanced winding patterns reduces energy waste and mechanical drag, supporting fuel economy.
- Smart Alternators: These electronically controlled units synchronize charging cycles to periods of engine deceleration or coasting, thereby reducing parasitic losses and emissions.
- Integrated Start-Stop Compatibility: Modern alternators ensure seamless operation during frequent engine restarts in start-stop systems.
- Thermal Management: Advanced cooling systems, including liquid-cooled models, allow alternators to deliver consistent output under prolonged load without overheating.
Manufacturer Comparison: Performance, Reliability, and Innovation
The global market for automotive alternators features a range of suppliers, each specializing in distinct technologies and serving varied automotive segments. The following table compares leading manufacturers on the criteria of output range, technological innovation, and warranty support:
| Manufacturer | Output Range (A) | Smart Alternator Tech | Warranty (Years) | Market Focus |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bosch | 90-200 | Yes | 2-3 | OEM Passenger, Premium, Commercial |
| Denso | 80-180 | Yes | 3 | Japanese OEMs, Hybrid, Commercial Fleet |
| Valeo | 100-220 | Advanced | 2 | European Fleet, Luxury, Eco Mode Vehicles |
| Remy | 70-160 | Not Available | 1-2 | Aftermarket, Commercial Retrofit |
| Hitachi | 85-170 | Yes | 2 | Asia-Pacific, Light Duty, Specialty |
Bosch and Denso consistently lead on technological innovation, offering alternators with real-time diagnostics and predictive maintenance features. Valeo’s advanced models integrate sophisticated software for start-stop and regenerative braking scenarios. Aftermarket suppliers like Remy focus on affordable retrofit solutions, addressing the needs of aging fleets.
Custom Alternator Solutions for Automotive Special Applications
As vehicle platform diversity expands, numerous industries require bespoke alternator configurations tailored to their operational environment. Custom alternators address the unique challenges posed by specialized vehicles:
- Commercial Trucks: Enhanced amperage outputs meet the demands of auxiliary systems (e.g., refrigeration units, lighting rigs).
- Off-road Vehicles: Alternators with dust-proof, water-sealed housings support agricultural, mining, and military applications.
- Electric and Hybrid Vehicles: Integration with regenerative braking and dual voltage networks requires high-performance, intelligent alternator modules.
- Emergency and Utility Fleets: Engineers specify quick-change, modular designs for rapid on-site swaps and field repairs.
Case Studies: Alternator Implementation Across Automotive Segments
Several notable real-world cases highlight the transformation enabled by advanced alternator technologies in both passenger and diesel-powered vehicles.
Case 1: Urban Delivery Fleet (Diesel-powered)
A leading European logistics company retrofitted its fleet of 200 delivery vans with high-capacity, liquid-cooled alternators. As a result, average electrical system downtime decreased by 70%, boosting overall fleet availability to 96%. Battery lifespan was extended by 18 months due to precise voltage regulation.
Case 2: Hybrid Passenger Cars
In collaboration with Denso, a Japanese automaker integrated smart alternators into its hybrid range. These alternators dynamically adjusted charging based on real-time energy demand and regenerative braking input. The vehicles demonstrated a validated 12% reduction in fuel consumption and a commensurate cut in CO2 emissions.
Case 3: Heavy-Duty Mining Equipment (Diesel Engine)
A mining contractor specified custom dust-sealed alternators with reinforced bearings. Post-installation, alternators operated flawlessly under high-vibration, high-dust conditions for over 14,000 hours before first maintenance, compared to an average 8,000 hours with previous models.
Altogether, these cases reinforce the significant gains in reliability, efficiency, and cost savings that result from the careful selection and application of the right car engine alternator technology.
The Transformative Future of Car Engine Alternator Technology
As automotive technology advances at an accelerating pace, the car engine alternator continues to evolve in its form and versatility. The accelerating transition to electrified platforms, the proliferation of intelligent diagnostics, and the growing integration of smart charging protocols are redefining the alternator’s role from a conventional power generator to a critical enabler of next-generation automotive functionality.
With regulations tightening around fuel economy and emissions, alternator manufacturers are expected to achieve even greater power densities and data-driven optimization. The adaptation of solid-state designs and potential on-board energy storage coworkers may unlock new paradigms in vehicle power management. Strategic investment in alternator selection, custom specification, and predictive maintenance will remain fundamental in realizing safer, more efficient, and more sustainable mobility—cementing the alternator's place at the heart of the modern automobile.
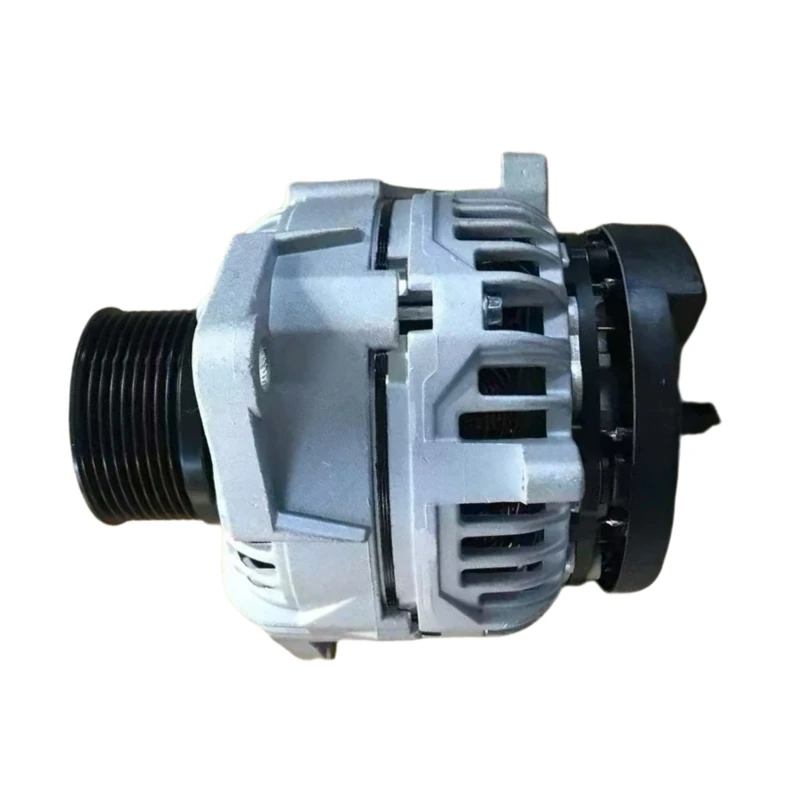

(car engine alternator)